In this article, we will talk about boilers and heat exchangers. Then we will examine one of the types of boilers.
Heat Exchanger
Definition: A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between two or more fluids. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes.
Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant.
U-tube heat exchanger is a form of tube and shell heat exchanger that is used in petroleum and chemical machinery. The tube box, casing, and tube buddle are the key components of a u-tube heat exchanger. Furthermore, drying is simple following the hydro test of the u-tube heat exchanger. read more

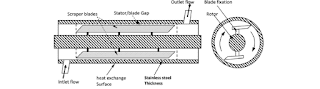
Boiler
Definition: A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid (generally water) is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.
System boiler: A system boiler, like a traditional boiler, requires a hot water storage tank but not a water container. This is due to the fact that the system’s main components, such as the expansion vessel and pump, are pre-assembled. System boilers are typically easier to maintain because they do not need a tank, eliminating the risk of leaks or damage. A machine boiler can be appropriate if you don’t have enough space for a tank but have several bathrooms.