The pump head or discharge head of a water pump is a measure of the power of a pump. The greater the pump head, the greater the pressure that the pump can generate. This statistic is measured in meters (or feet) and is calculated by placing a tube on a pump’s discharge and measuring the maximum height to which it can pump water.
This was a brief definition of the pump head. In the continuation of the article, we will carefully examine the pump head and compare it with other components, so stay tuned and read this article to the end.

A positive-displacement pump makes a fluid move by trapping a fixed amount and forcing (displacing) that trapped volume into the discharge pipe.
Some positive-displacement pumps use an expanding cavity on the suction side and a decreasing cavity on the discharge side. Liquid flows into the pump as the cavity on the suction side expands and the liquid flows out of the discharge as the cavity collapses. The volume is constant through each cycle of operation. Read more
The table below includes minimum efficiency requirements for the following ENERGY STAR-qualified covered product categories: air-source heat pumps (residential) and geothermal heat pumps (residential).
| equipment Type | Size Category | Heating Section Type | Subcategory or Rating Condition | Minimum Efficiency |
| Air-cooled (cooling mode) | <65,000 Btu/h | All | Split system | 15.0 SEER; 12.5 EER; 8.5 HSPF (single phase) |
| Single package | 15.0 SEER; 12.0 EER; 8.2 HSPF (single phasea) | |||
| ≥65,000 Btu/h and <135,000 Btu/h | Electric resistance (or none) | Split system and single package | 11.8 EER; 12.8 IEER; 3.4 COP at 47ºF |
Total head
A much more useful measure of the head is the difference between the liquid level in the suction tank and the head in the vertical discharge pipe. This number is known as the “total head” that the pump can produce.
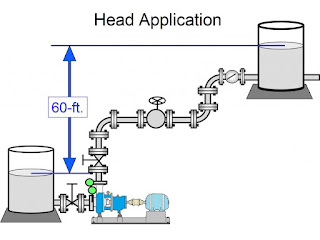
Increasing the level of the liquid in the suction tank will give rise to the increased heat, and decreasing the level will give rise to a lower head. Pump manufacturers and suppliers often won’t tell you how much head a pump can produce, because they can’t predict what the height of the liquid in your suction tank will be. Instead, they will report the total head of pump, the difference in height between the level of liquid in the suction tank, and the height of a column of water that the pump can achieve. Click to read more information.
References:
https://www.linquip.com/blog/what-is-head-of-a-pump/